COMPUTER NETWORKS
CONE Lab - Link - Numerical exercises
Problem
12 (Ch. 5 of Computer Networking by J.F. Kurose and K.W.
Ross)
Consider
three LANs interconnected by two routers, as shown in the diagram below.
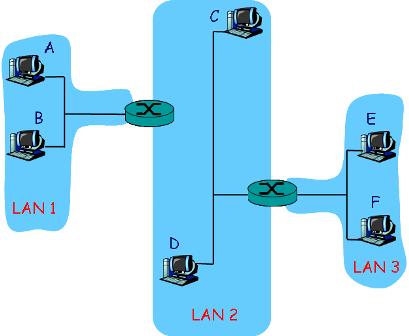
a) Redraw
the diagram to include adapters.
b) Assign IP addresses to all of the interfaces. For LAN 1 use addresses
of the form 111.111.111.xxx ; for LAN 2 uses addresses of the form 122.222.222.xxx
; and for LAN 3 use addresses of the form 133.333.333.xxx .
c) Assign LAN addresses to all of the adapters.
d) Consider sending an IP datagram from host A to host F. Suppose all
the ARP tables are up-to-date. Enumerate all the steps as done for the
single-router example in section 5.3.2.
e) Repeat (d), now assuming that the ARP table in the sending host is
empty (and the other tables are up-to-date).
Problem
13 (Ch. 5of Computer Networking, 2nd ed. by J.F. Kurose
and K.W. Ross)
Recall
that with the CSMA/CD protocol, the adapter waits K*512 bit times after
a collision, where K is drawn randomly. For K=100, how long does the adapter
wait until returning to Step 2 for a 10 Mbps Ethernet? For a 100 Mbps
Ethernet?
Problem
14 (Ch. 5of Computer Networking, 2nd ed. by J.F. Kurose
and K.W. Ross)
Suppose nodes A and B are on the same 10 Mbps Ethernet segment,
and the propagation delay between the two nodes is 225 bit times. Suppose
node A begins transmitting a frame, and before it finishes station B begins
transmitting a frame. Can A finish transmitting before it detects that
B has transmitted? Why or why not? If the answer is yes, then A incorrectly
believes that its frame was successfully transmitted without a collision.
Hint:
Suppose at time t=0 bit times, A begins transmitting a frame. In the worst
case, A transmits a minimum size frame of 512+64 bit times. So A would
finish transmitting the frame at t=512+64 bit times. Thus the answer is
no if B's signal reaches A before bit time t=512+64 bits. In the worst
case, when does B's signal reach A?